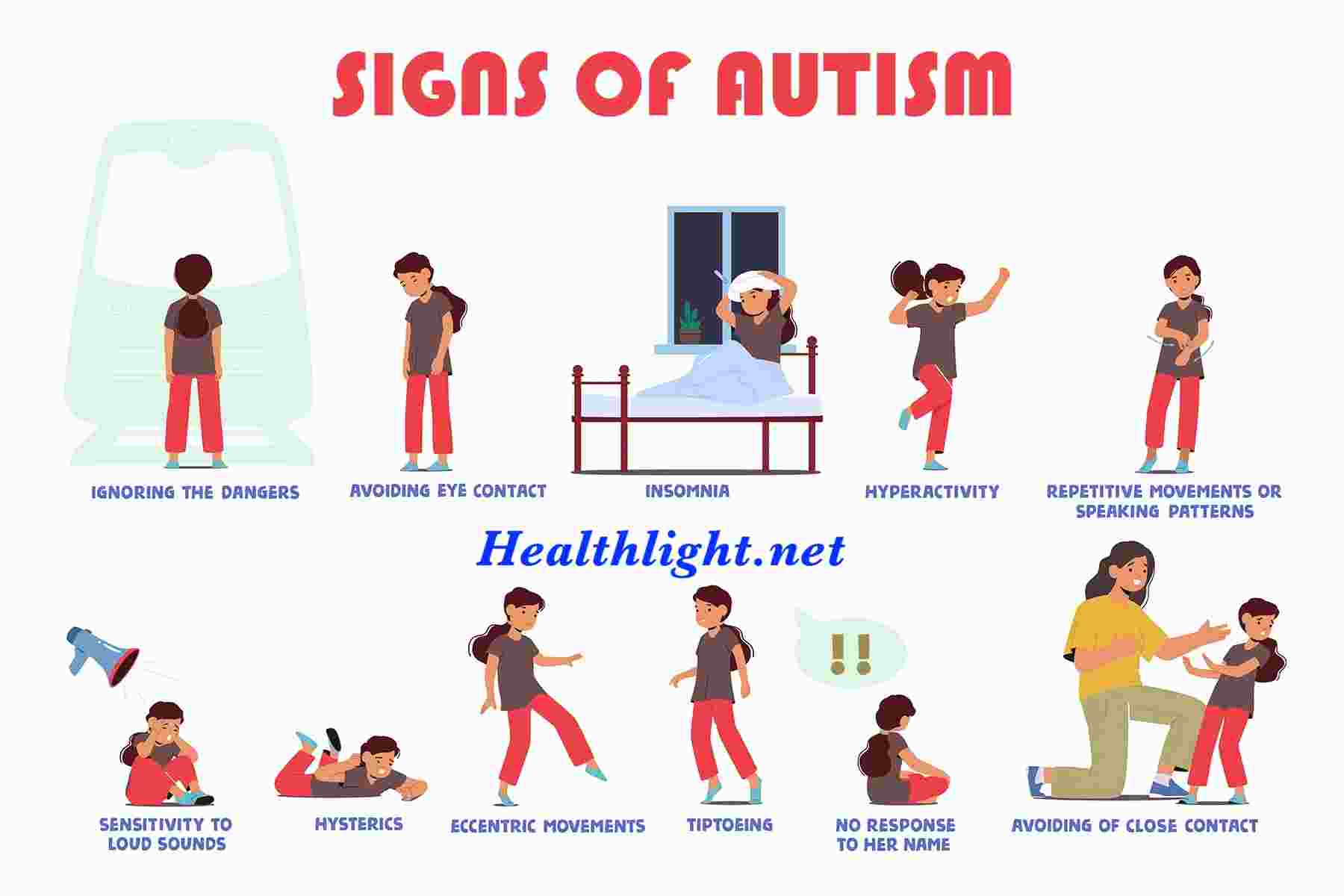
Magnesium is one of the most important minerals in the human body, playing a role in over 300 biochemical reactions. While it is found in foods like leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains, many adults don’t get enough through diet alone. Among the different supplement forms, Magnesium Glycinate stands out because it is well absorbed and gentle on the stomach.
This article takes a deep dive into magnesium glycinate, its benefits, uses, dosage, side effects, and why many people prefer it over other forms of magnesium.
What Is Magnesium Glycinate?
Magnesium Glycinate is a compound made of magnesium and glycine, an amino acid. This combination allows the body to absorb magnesium more effectively compared to some other forms such as magnesium oxide or magnesium sulfate. Because it is gentle on digestion, it is often recommended for people who cannot tolerate harsher magnesium supplements.
Why Magnesium Matters?
Magnesium supports several critical functions in the body, including:
- Energy production.
- Muscle and nerve function.
- Blood sugar control.
- Bone health.
- DNA and protein synthesis.
Without enough magnesium, individuals may experience symptoms such as fatigue, muscle cramps, anxiety, and poor sleep. Long-term deficiency can contribute to chronic conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and osteoporosis.
Benefits of Magnesium Glycinate:
Supports Relaxation and Reduces Stress:
Glycine, the amino acid in magnesium glycinate, has calming properties. Together with magnesium, it helps regulate neurotransmitters that affect mood and relaxation. Many people take it to ease stress, tension, and feelings of restlessness.
Improves Sleep Quality:
This supplement is popular as a natural sleep aid. It may help you fall asleep faster and improve overall sleep quality by promoting relaxation and regulating melatonin production.
Gentle on the Stomach:
Unlike other magnesium forms that may cause diarrhea or digestive upset, magnesium glycinate is well tolerated. This makes it a good option for people with sensitive digestion.
Supports Muscle Function:
Athletes and active adults often use it to prevent muscle cramps and aid recovery. Magnesium plays a vital role in muscle contraction and relaxation, making it important for both exercise performance and daily movement.
Promotes Heart Health:
Magnesium helps regulate heartbeat, blood pressure, and overall cardiovascular function. Adequate intake may reduce the risk of hypertension and heart disease.
May Reduce Symptoms of Anxiety:
Some studies suggest that magnesium can calm the nervous system and reduce symptoms of mild anxiety. Since stress and anxiety are often linked with magnesium deficiency, supplementation may be especially beneficial.
Bone and Joint Support:
Magnesium works with calcium and vitamin D to strengthen bones. For adults concerned about osteoporosis or age-related bone loss, magnesium glycinate is an excellent addition to a bone-health plan.
Supports Blood Sugar Balance:
This supplement may improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels, making it useful for people with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
Who May Benefit from Magnesium Glycinate?
Certain groups are more likely to experience magnesium deficiency and may benefit from supplementation:
- Adults under high stress.
- People with poor sleep.
- Athletes or those with muscle cramps.
- Individuals with digestive disorders like IBS or Crohn’s.
- Older adults (absorption decreases with age).
- People with high blood pressure or diabetes.
Natural Sources of Magnesium:
Although supplementation is helpful, getting magnesium from foods should be a priority. Good dietary sources include:
- Spinach and kale.
- Pumpkin seeds and sunflower seeds.
- Almonds and cashews.
- Black beans and lentils.
- Avocados.
- Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice.
Eating a balanced diet combined with magnesium glycinate supplementation ensures your body maintains optimal levels.
Recommended Dosage:
The dosage depends on age, sex, and health needs. General guidelines for adults are:
- Men: 400-420 mg per day.
- Women: 310-320 mg per day.
- Pregnant women: 350-360 mg per day.
Supplements usually come in capsules containing around 100-200 mg of magnesium glycinate. It’s best to start with a lower dose and increase if needed, under medical supervision.
Best Time to Take Magnesium Glycinate:
- For sleep and relaxation: Take in the evening, about 1–2 hours before bed.
- For muscle recovery: Take after exercise with a meal.
- For general wellness: Take with food to improve absorption.
Consistency is more important than timing, so choose a routine that fits your lifestyle.
Possible Side Effects:
Magnesium glycinate is generally safe for most adults. However, excessive intake can cause:
- Loose stools (rare with glycinate form).
- Nausea.
- Stomach upset.
- Low blood pressure (in very high doses).
People with kidney disease should be cautious, as their bodies may not clear excess magnesium effectively. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplementation.
Comparing Magnesium Glycinate to Other Forms:
- Magnesium Oxide: Cheaper but less bioavailable; often used for constipation.
- Magnesium Citrate: Better absorption than oxide but can cause diarrhea.
- Magnesium Malate: May help with muscle pain and fatigue.
- Magnesium Threonate: Known for cognitive benefits but more expensive.
- Magnesium Glycinate: Highly absorbable, gentle, and excellent for sleep and relaxation.
Tips for Maximizing Benefits:
- Take magnesium glycinate with meals to improve absorption.
- Pair with vitamin D and calcium for stronger bone health.
- Avoid taking it with high-dose zinc or iron, which may interfere with absorption.
- Stay hydrated to support mineral balance in the body.
- Keep track of your intake through both diet and supplements.
When to See a Doctor?
Consult a healthcare professional if you:
- Experience persistent fatigue, muscle cramps, or irregular heartbeat.
- Have existing health conditions like kidney disease or heart issues.
- Take prescription medications, as magnesium can interact with certain drugs (like antibiotics or blood pressure medicines).
Final Thoughts:
Magnesium Glycinate is one of the most effective and well-tolerated ways to increase magnesium levels. From improving sleep and reducing stress to supporting muscle and heart health, it offers numerous benefits for adults. Because it is gentle on digestion, it’s suitable even for people with sensitive stomachs.
Adding magnesium-rich foods to your diet, combined with the right supplement, can significantly improve your overall well-being. As with any supplement, consult a healthcare professional to determine the right dose for your needs.
FAQs
Is Magnesium Glycinate safe for daily use?
Yes, it is safe for most adults when taken within recommended limits.
Can it help with insomnia?
Many people find it improves sleep quality by calming the nervous system.
How long does it take to notice results?
Some effects, like relaxation, may be felt within days, while others, like bone health, take weeks or months.
Can pregnant women take magnesium glycinate?
Yes, but they should consult a doctor to determine the right dosage.
Is magnesium glycinate better than citrate?
It is better tolerated by the stomach and more effective for stress and sleep, while citrate is commonly used for digestion support.