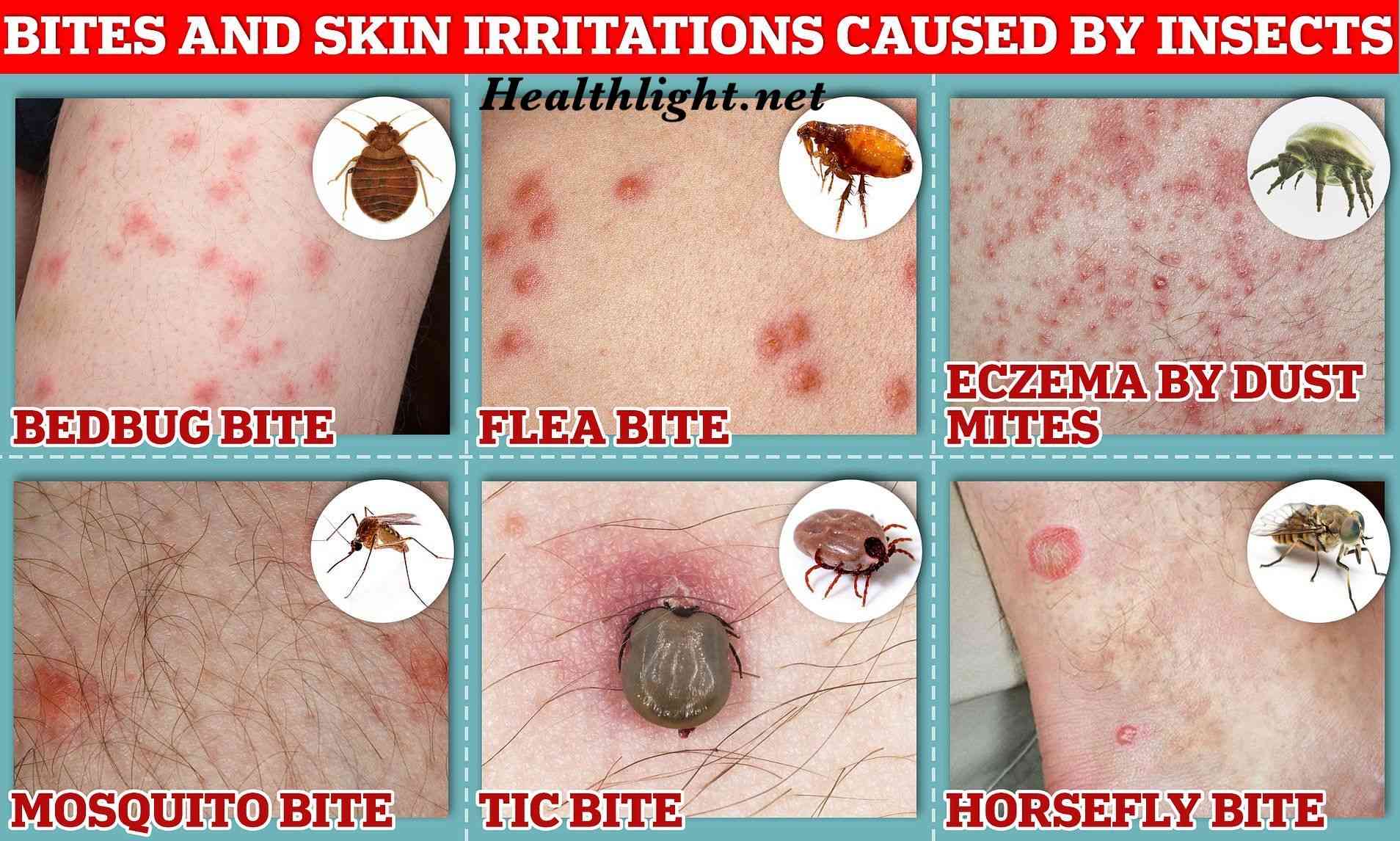
Bed Bugs are small, reddish-brown insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals, usually at night. Though they do not spread diseases directly, their bites can cause itching, discomfort, allergic reactions, and psychological stress. Bed bug infestations are becoming increasingly common in homes, hotels, and public places worldwide.
This article provides a complete guide to Bed Bugs Bites, covering how to identify them, their bites, available treatments, and effective prevention strategies.
What is Bed Bugs?
Bed bugs are tiny, wingless insects that hide in cracks, mattresses, furniture, and clothing. They are nocturnal and typically bite people while they are sleeping. Adult bed bugs are about the size of an apple seed, while nymphs (younger bugs) are smaller and lighter in color.
- Color: Reddish-brown.
- Size: 5–7 mm (about a grain of rice).
- Lifespan: 6–12 months.
- Feeding: Blood meals every 5–10 days.
These pests reproduce quickly, with females laying hundreds of eggs during their lifetime.
How to Identify Bed Bugs?
Correct identification is the first step in dealing with an infestation. Here’s how you can spot them:
Physical Signs:
- Small reddish-brown insects in mattress seams, bed frames, or upholstered furniture.
- Tiny white eggs or eggshells (about 1 mm).
- Shed skins from growing nymphs.
- Rust-colored spots on sheets or mattresses (caused by crushed bugs or fecal stains).
Bed Bugs Bites Appearance:
- Small, red, itchy welts on the skin.
- Often appear in clusters or straight lines.
- Commonly found on arms, legs, neck, and face.
- May take a few days to show up after being bitten.
Smell:
A heavy infestation can produce a musty, sweet odor, similar to overripe berries.
Bed Bug Bites: Symptoms & Reactions:
Bed bug bites vary from person to person. Some may show no reaction, while others develop severe itching or allergic responses.
Common Bite Symptoms:
- Red, swollen welts with a darker center
- Severe itching, especially at night
- Burning or stinging sensation
- Small blisters in severe cases
Complications:
- Secondary infections from scratching (impetigo, cellulitis).
- Allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
- Anxiety and insomnia due to infestation stress.
Treatment for Bed Bug Bites:
There is no special medication required for most bed bug bites, but symptoms can be managed at home.
Home Remedies:
- Cold compresses: Reduce swelling and itching.
- Over-the-counter antihistamines: Relieve itching and allergic reactions.
- Hydrocortisone cream: Eases redness and irritation.
- Aloe vera or calamine lotion: Provides soothing relief.
When to See a Doctor?
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe allergic reaction (difficulty breathing, swelling of face or throat).
- Signs of infection (pus, warmth, or severe pain at the bite site).
- Extensive skin reactions that don’t improve with home care.
How to Get Rid of Bed Bugs (Treatment of Infestation)?
Killing bed bugs requires a comprehensive approach since they are resilient and can survive for months without feeding.
Clean and Declutter:
- Wash all bedding, curtains, and clothing in hot water (above 120°F).
- Dry items on the highest heat setting for at least 30 minutes.
- Vacuum mattresses, bed frames, and carpets thoroughly.
Use Heat Treatment:
Bed bugs cannot survive extreme heat. Professional exterminators may use steam cleaning or specialized heaters to kill them.
Insecticides:
Certain EPA-approved insecticides can be effective, including:
- Pyrethrins and pyrethroids (most common).
- Desiccants like diatomaceous earth (dehydrate bugs).
- Neonicotinoids and insect growth regulators (target reproductive cycles).
Professional Pest Control:
Severe infestations often require licensed pest control experts who use a combination of chemical and non-chemical methods.
Prevention of Bed Bugs:
Preventing bed bugs is easier than getting rid of them. Follow these steps to protect your home:
- Inspect Second-Hand Furniture: Check thoroughly before bringing it home.
- Protect Your Mattress: Use a bed bug-proof encasement to prevent infestations.
- Reduce Clutter: Eliminate hiding spots like piles of clothes and papers.
- Travel Smart: Inspect hotel beds and furniture, keep luggage off the floor, and wash clothes immediately after returning.
- Seal Cracks and Gaps: Prevent bugs from hiding in walls, baseboards, or furniture.
- Regular Cleaning: Vacuum carpets, furniture, and bedding frequently.
Final Words:
Bed Bugs Bites are persistent pests that cause discomfort, stress, and skin irritation. Understanding their bites, identification, treatment, and prevention is essential to avoid infestations. While home remedies may help with mild cases, large infestations usually require professional extermination.
By practicing good hygiene, inspecting your surroundings, and using preventive strategies, you can protect yourself and your home from these unwelcome visitors.