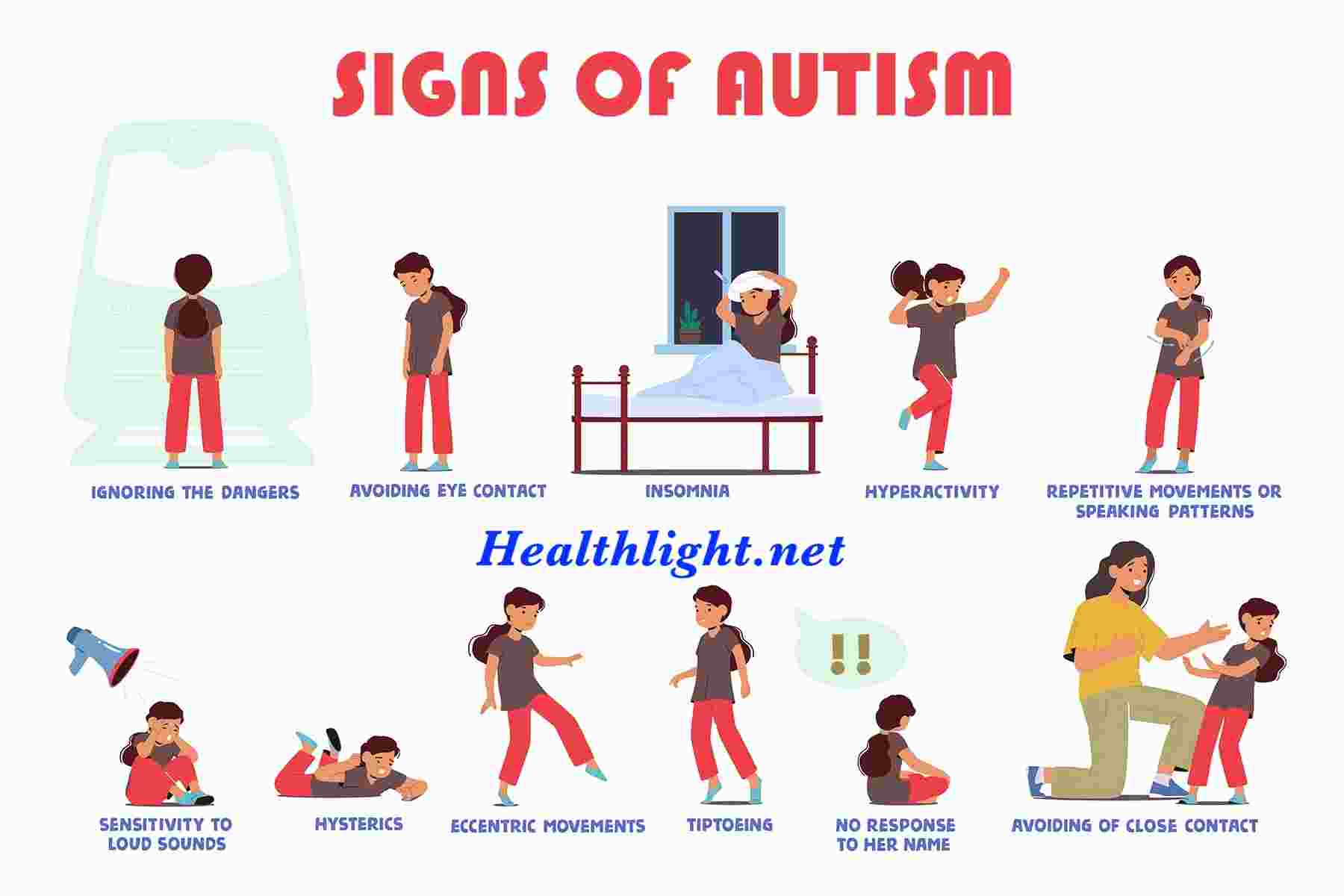
Autism is a developmental condition that influences how people interact, communicate, learn, and behave. It’s called a spectrum disorder because symptoms can range from mild to severe, and no two individuals with autism are exactly alike.
What Is Autism?
Autism, also known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a developmental condition that influences how a person interacts, communicates, learns, and behaves. It is called a spectrum because symptoms and abilities can vary widely some people may need significant daily support, while others live independently and excel in specific areas.
ASD typically appears before the age of 3 and lasts throughout a person’s life. While some individuals need significant support in daily life, others live independently, excel in school or work, and build meaningful relationships.
Autism Symptoms:
Autism symptoms usually appear in early childhood, though some may not be recognized until later in life. Symptoms differ across children and adults but often fall into two main categories.
Social and Communication Challenges:
- Limited eye contact.
- Difficulty understanding tone, gestures, or facial expressions.
- Trouble forming friendships.
- Preferring solitude over group play.
- Delayed speech or unusual speech patterns.
Repetitive Behaviors and Interests:
- Repeating words, phrases, or actions.
- Strong attachment to routines.
- Intense focus on specific interests (like trains, numbers, or maps).
- Rocking, flapping hands, or spinning objects (stimming behaviors).
Sensory Sensitivities:
- Overreaction to lights, sounds, textures, or smells.
- Unusual tolerance or intolerance to pain.
- Seeking repetitive sensory input, like spinning or touching objects.
Autism in Adults:
Signs may look different in adults and include:
- Difficulty understanding social cues or sarcasm.
- Anxiety in group settings.
- Preference for routine and order.
- Appearing blunt or “rude” unintentionally.
- Trouble expressing emotions.
Autism in Children:
Parents and caregivers may notice:
- No response to their name by 9 months.
- Limited gestures like pointing or waving.
- Not showing interest in playing with other children.
- Delayed speech development.
- Repetitive play, like lining up toys.
- Extreme distress when routines change.
Types of Autism:
Before the DSM-5 grouped them under one diagnosis, autism was divided into several subtypes:
- Asperger’s Syndrome: Milder autism, with average or above-average intelligence but difficulties in social skills.
- Autistic Disorder: What most people once thought of as “classic autism,” with significant challenges in communication and behavior.
- Childhood Disintegrative Disorder: Rare, with normal development for a few years followed by sudden loss of skills.
- Pervasive Developmental Disorder – Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS): When symptoms didn’t fully match other categories but still indicated developmental differences.
Now, all of these are included under Autism Spectrum Disorder to emphasize the wide range of experiences.
What Causes Autism?
The exact cause of autism remains unknown, but research suggests a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors:
- Autism often runs in families.
- Certain gene variations may affect brain development.
- Rare mutations (e.g., ADNP gene) can directly cause autism in a small percentage of cases.
Environmental Influences:
- Advanced parental age.
- Low birth weight.
- Complications during pregnancy or birth.
- Prenatal exposure to toxins or infections.
Myths Debunked:
- Vaccines do not cause autism. Scientific studies repeatedly confirm no link between vaccines and autism.
Autism Testing and Diagnosis:
Autism can be diagnosed at any age, though symptoms often appear early.
For Children:
- Developmental Screening: Regular checkups at 9, 18, and 24 months screen for delays.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: If delays are found, specialists like child psychologists or developmental pediatricians perform detailed assessments.
Tests may include:
- Observing behavior and social interaction.
- Speech and language evaluations.
- Cognitive and developmental testing.
- Hearing and vision checks.
- Genetic testing (if needed).
For Adults:
Adults may seek diagnosis if lifelong challenges begin to interfere with work, relationships, or daily life. Specialists conduct interviews, questionnaires, and behavior assessments.
Autism Treatment Options:
There is no cure for autism, but early intervention and therapies can significantly improve quality of life. Treatment plans are individualized.
Therapies:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): Teaches positive behaviors and reduces harmful ones.
- Speech Therapy: Builds communication skills.
- Occupational Therapy: Supports daily living skills and manages sensory issues.
- Social Skills Training: Improves interaction and emotional connections.
Medications:
Doctors may prescribe medicines to manage related symptoms like anxiety, ADHD, or aggression.
Lifestyle & Complementary Support:
- Structured routines at home and school.
- Music, art, or animal-assisted therapy.
- Balanced diet and good sleep hygiene.
Living With Autism:
Many people with autism live independent, successful lives. They may excel in fields such as science, art, technology, or music. Increasing awareness and acceptance of neurodiversity is helping communities value the unique strengths of autistic individuals.
Support from family, schools, workplaces, and society makes a huge difference in helping people with autism thrive.
Conclusion:
Autism Spectrum Disorder is a lifelong condition that affects communication, learning, and behavior. While it varies widely from person to person, early detection, therapy, and family support can make a life-changing difference.
Understanding autism helps create a more inclusive society where people are valued for their unique perspectives and strengths.
FAQs:
Can children with autism live a normal life?
Yes. With support and therapies, children with autism can reach their full potential and live fulfilling lives.
What is autism level 2?
Level 2 autism requires substantial support for social and communication skills, as well as help adapting to daily routines.
Is autism genetic?
Genetics play a strong role, though environmental factors also contribute.
What is an autism test?
Here’s no single test. Diagnosis involves behavioral observations, developmental screenings, and specialist evaluations.
Can autism be cured?
There is no cure, but therapies and interventions greatly improve outcomes.