Lower back pain is one of the most common health complaints worldwide. Millions of people experience it at some point in their lives, making it a leading reason for missed work, reduced mobility, and long-term discomfort. In this latest guide, we will explore the major causes of lower back pain, the common symptoms, and the most effective treatment options available today.
What is Lower Back Pain?
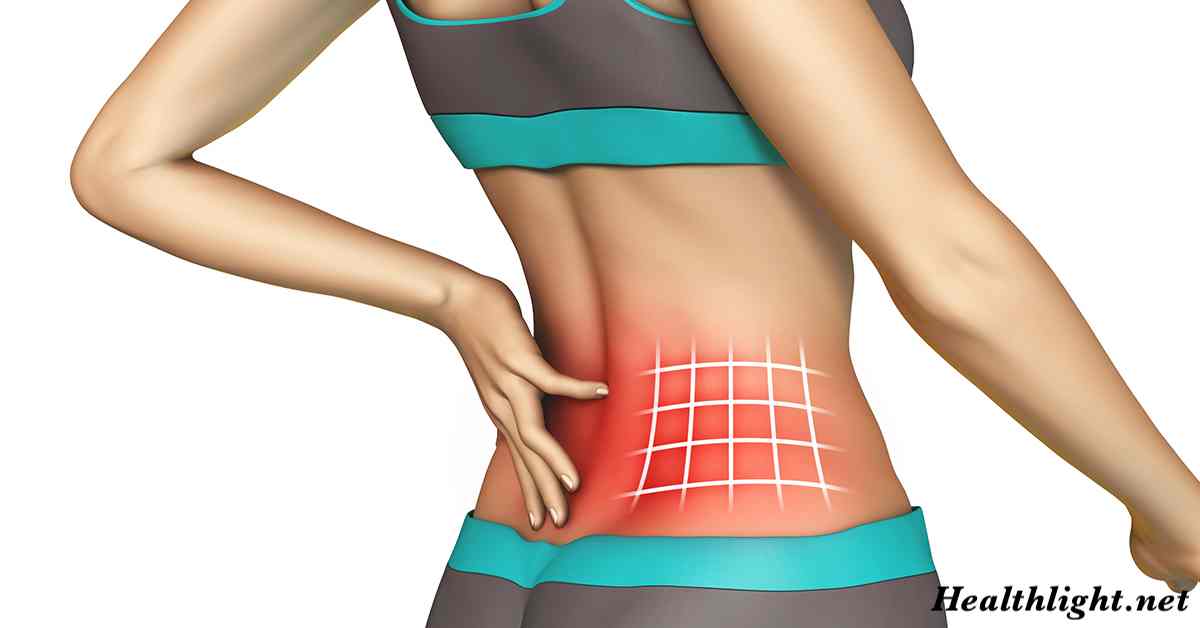
The lower back, also known as the lumbar spine, carries much of the body’s weight and plays a critical role in movement. Because of this constant stress, it is highly vulnerable to injuries, degenerative changes, and muscle strains. Lower back pain can range from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations that limit daily activities.
Common Causes of Lower Back Pain:
Muscle or Ligament Strain:
Sudden movements, lifting heavy objects, or poor posture can strain muscles and ligaments in the lower back. This is the most frequent cause of temporary back pain.
Herniated or Bulging Discs:
The discs between the vertebrae act as cushions. When these discs become damaged or slip out of place, they press on nearby nerves, causing intense pain that may radiate down the legs.
Degenerative Disc Disease:
With age, spinal discs lose their flexibility and ability to absorb shock. This condition often leads to chronic lower back pain.
Arthritis and Spinal Stenosis:
Osteoarthritis can affect the lower spine, causing inflammation and stiffness. In severe cases, it leads to spinal stenosis, where the spinal canal narrows and compresses nerves.
Poor Posture and Sedentary Lifestyle:
Sitting for long hours, especially with poor posture, weakens back muscles and increases stress on the lumbar spine.
Injuries and Accidents:
Falls, sports injuries, or car accidents can damage the spine, muscles, or ligaments, leading to acute or chronic pain.
Other Medical Conditions:
Conditions like scoliosis, osteoporosis, kidney infections, or tumors can also cause lower back pain, though these are less common.
Symptoms of Lower Back Pain:
Lower back pain symptoms vary depending on the underlying cause. Common signs include:
- Constant dull ache or sharp stabbing pain in the lower back.
- Pain that worsens with sitting, bending, or lifting.
- Muscle spasms or stiffness.
- Pain radiating into the buttocks or down the legs (sciatica).
- Reduced flexibility and difficulty standing upright.
- Numbness or tingling in legs or feet in severe cases.
If lower back pain is accompanied by loss of bladder control, fever, or unexplained weight loss, immediate medical attention is necessary.
Risk Factors for Lower Back Pain:
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing lower back pain:
- Age (commonly affects people over 40).
- Lack of exercise or weak core muscles.
- Excess body weight adding pressure on the spine.
- Physically demanding jobs involving heavy lifting.
- Smoking, which reduces blood flow to spinal tissues.
- Family history of spinal problems.
Effective Treatment Options for Lower Back Pain (2025 Updates):
Treatment depends on the severity and root cause of the pain. Modern approaches combine self-care, medical treatments, and lifestyle changes.
Self-Care and Home Remedies:
- Rest and activity balance: Short rest periods followed by light movement help reduce stiffness.
- Hot and cold therapy: Ice packs reduce inflammation, while heat pads relax tight muscles.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Ibuprofen and acetaminophen are often effective.
Physical Therapy and Exercise:
Physical therapists design stretching and strengthening programs to improve posture, core stability, and flexibility. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, and yoga are highly recommended.
Medications:
Doctors may prescribe muscle relaxants, stronger painkillers, or anti-inflammatory drugs for severe cases.
Minimally Invasive Treatments:
Injections such as corticosteroids provide temporary relief for inflamed nerves. These are often recommended when pain does not respond to conservative measures.
Surgery:
Surgical options like discectomy, laminectomy, or spinal fusion are reserved for cases where nerve compression causes severe pain or mobility issues. Advances in 2025 allow for minimally invasive spine surgeries, which reduce recovery time.
Alternative Therapies:
Acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy are increasingly popular as complementary treatments for lower back pain.
How to Protect Your Lower Back?
Preventing lower back pain is possible with consistent lifestyle choices:
- Maintain good posture when sitting and standing.
- Use ergonomic chairs and workstations.
- Exercise regularly to strengthen core muscles.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects incorrectly; bend your knees instead of your back.
- Maintain a healthy body weight.
- Quit smoking to improve spinal health.
When to See a Doctor?
Most lower back pain improves within a few weeks with self-care. However, medical help is necessary if:
- Pain persists longer than 6 weeks.
- Pain radiates to the legs or causes numbness.
- Severe pain follows an accident or injury.
- Pain is accompanied by fever, chills, or sudden weight loss.
Early diagnosis and treatment improve recovery and prevent long-term complications.
Latest 2025 Insights on Lower Back Pain:
In 2025, healthcare providers emphasize a holistic approach to managing lower back pain. Combining modern medicine, physical therapy, ergonomic solutions, and preventive care ensures better results. Additionally, AI-powered posture monitoring devices and wearable fitness trackers help individuals maintain proper alignment and avoid strain throughout the day.
Conclusion:
Lower back pain is a widespread condition that affects people of all ages. While it can be disruptive, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options allows individuals to take control of their health. With proper care, exercise, and preventive measures, most cases of lower back pain can be managed effectively, leading to improved quality of life in 2025 and beyond.